In a period of rapid-fire technological advancement, the Internet of Bodies (IoB) is arising as a ground- breaking development poised to revise healthcare. The IoB refers to a network of connected bias, including wearables and implantable, that collect, transmit, and dissect physiological and biometric data. This confluence of healthcare and technology offers unknown openings for individualized drug, real- time monitoring, and bettered patient issues.
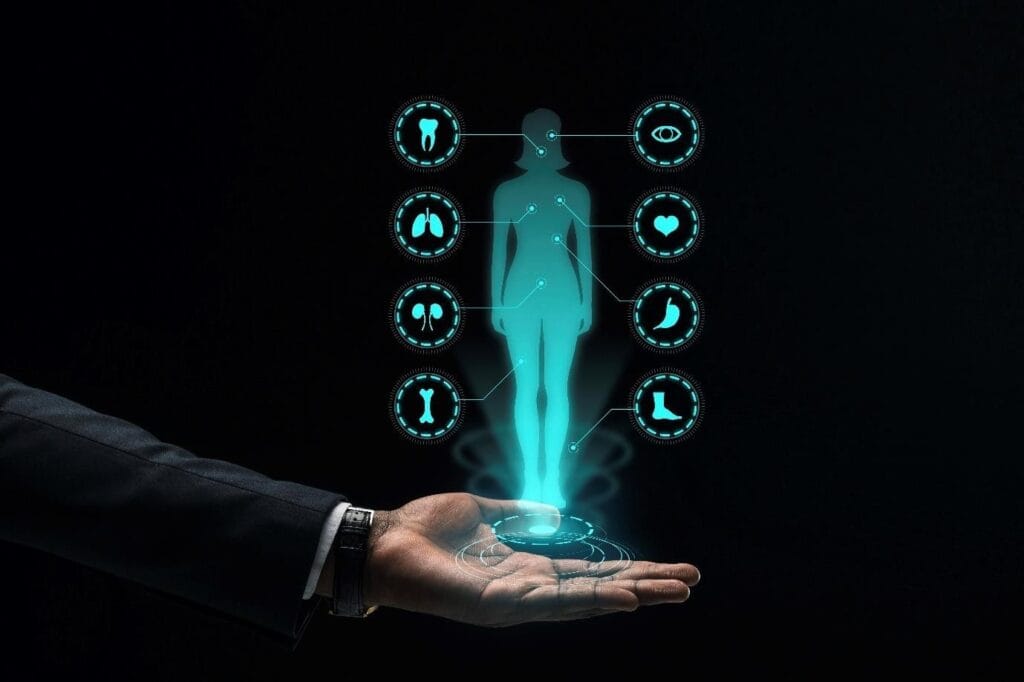
In a period of rapid-fire technological advancement, the Internet of Bodies (IoB) is arising as a ground- breaking development poised to revise healthcare. The IoB refers to a network of connected bias, including wearables and implantable, that collect, transmit, and dissect physiological and biometric data. This confluence of healthcare and technology offers unknown openings for individualized drug, real- time monitoring, and bettered patient issues.
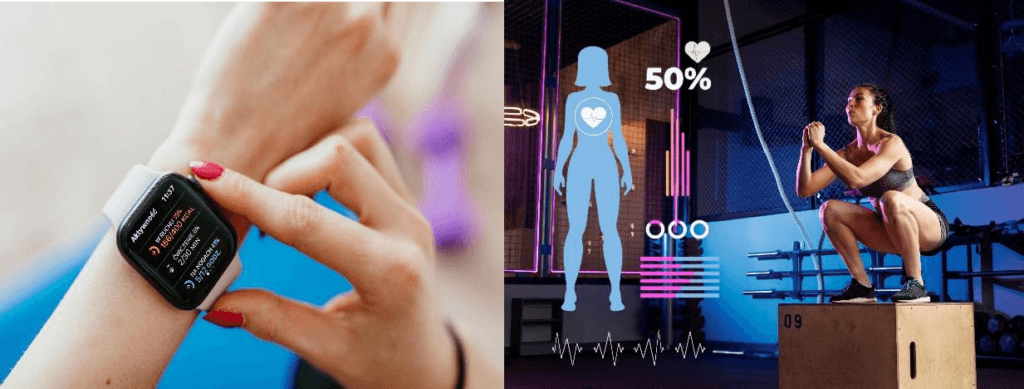
In a period of rapid-fire technological advancement, the Internet of Bodies (IoB) is arising as a ground- breaking development poised to revise healthcare. The IoB refers to a network of connected bias, including wearables and implantable, that collect, transmit, and dissect physiological and biometric data. This confluence of healthcare and technology offers unknown openings for individualized drug, real- time monitoring, and bettered patient issues.

Challenges and Ethical Considerations
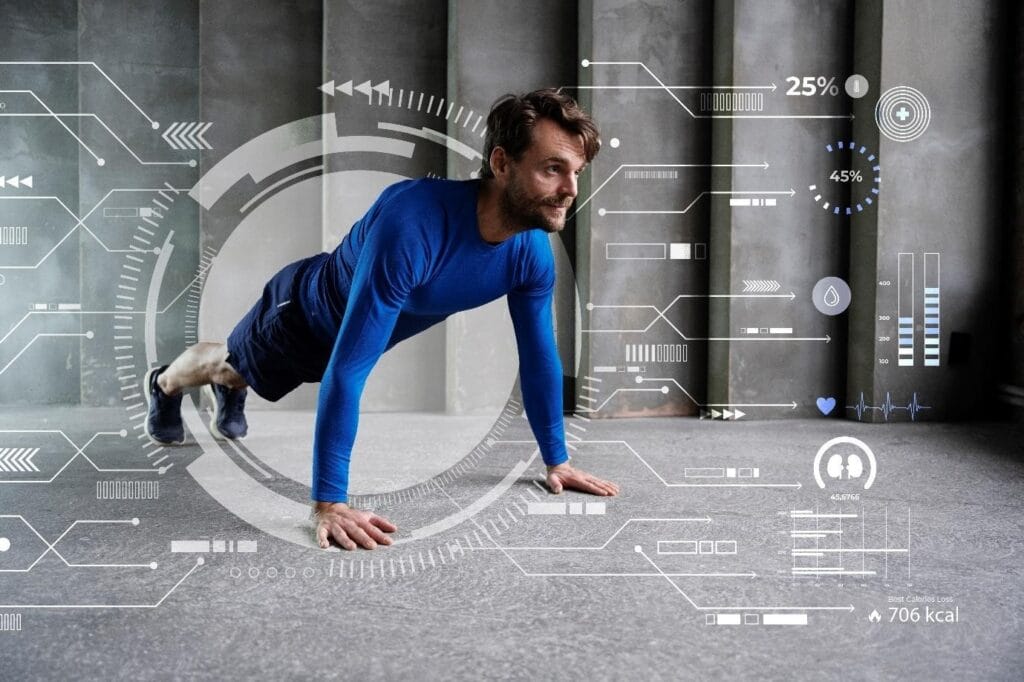
While the IoB holds great pledge, it also presents several challenges and ethical enterprises that need to be addressed
- The sensitive nature of health data collected by IoB bias necessitates robust sequestration and security measures. Data protection and precluding unauthorized access are critical to maintaining patient trust and confidentiality.
- The delicacy and trust ability of data from IoB bias are consummate. Inaccurate or defective data can lead to incorrect judgments or unhappy treatments, posing pitfalls to patient safety.
- The nonsupervisory geography for IoB bias is still evolving. Clear guidelines and norms are demanded to ensure the safety, efficacity, and ethical use of the technology.
- The use of implantable bias raises ethical questions about fleshly autonomy and concurrence. It’s essential to ensure that cases are completely informed and accord to the use of similar bias.
The Future of IoB in Healthcare
The future of IoB in healthcare is promising, with ongoing advancements in technology driving new possibilities. Then are some awaited developments.
1. Integration with AI and Machine Learning
The integration of AI and machine literacy with IoB bias will enhance data analysis and prophetic capabilities. This will enable more accurate judgments, substantiated treatment plans, and visionary health operations.
2. Development of Advanced Biomaterials
inventions in biomaterials will lead to more sophisticated implantable biases that are biocompatible, durable, and capable of complex functions, similar to towel juvenescence and medicine delivery.
3. Expansion of Telemedicine
The growth of telemedicine will be supported by IoB bias, enabling further comprehensive remote care results. This will upgrade access to healthcare, particularly in underserved and remote areas.
4. Enhanced Patient Engagement
IoB bias will empower cases to take an active part in managing their health. stoner-friendly interfaces and real-time feedback will encourage healthier cultures and adherence to treatment plans.
5. Collaboration and Data participation
bettered interoperability and data sharing between IoB bias and healthcare systems will grease better collaboration of care. cooperative sweat between technology companies, healthcare providers, and controllers will drive the development of standardized protocols and stylish practices.

The Internet of Bodies ( IoB) represents a transformative shift in healthcare, using the power of wearables and implantables to enhance patient care, ameliorate issues, and drive medical invention. As technology continues to evolve, the eventuality for IoB to revise healthcare is immense. still, it’s essential to address the associated challenges and ethical considerations to insure the safe, effective, and indifferent use of these technologies. By embracing the IoB, we can look forward to a future where healthcare is more individualized, visionary, and accessible than ever ahead.